Treatment
Plutchik’s wheel of emotions
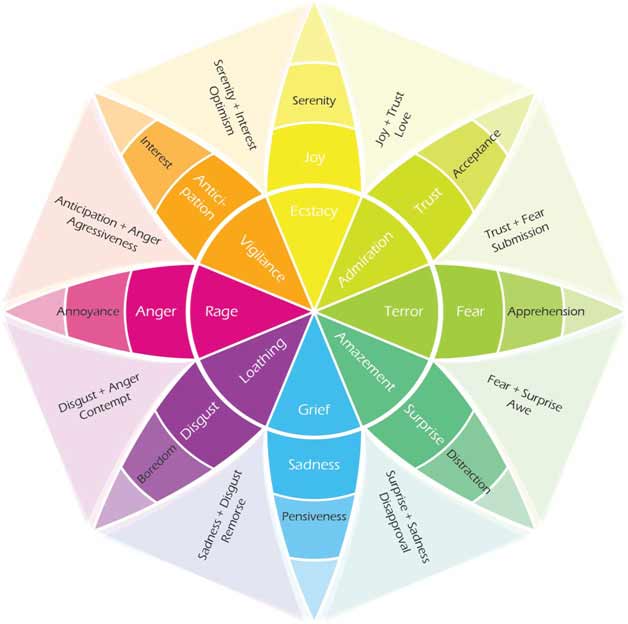
• Primary dyad = one petal apart = Love = Joy + Trust
• Secondary dyad = two petals apart = Envy = Sadness + Anger
• Tertiary dyad = three petals apart = Shame = Fear + Disgust
• Opposite emotions = four petals apart = Anticipation ≠ Surprise

Emotions also come in a variety of intensities, for example, Distraction is a mild form of Surprise, and Rage is an intense form of Anger. Weaker emotions lay among the outer circles and stronger emotions bloom in the middle. The kinds of relation between each pair of emotions follow below:
Mild emotion |
Mild opposite |
Basic emotion |
Basic opposite |
Intense emotion |
Intense opposite |
Serenity |
Pensiveness |
Joy |
Sadness |
Ecstasy |
Grief |
Acceptance |
Boredom |
Trust |
Disgust |
Admiration |
Loathing |
Apprehension |
Annoyance |
Fear |
Anger |
Terror |
Rage |
Distraction |
Interest |
Surprise |
Anticipation |
Amazement |
Vigilance |
Dyads (Combinations)
Human feelings |
Emotions |
Opposite feelings |
Emotions |
Optimism |
Anticipation + Joy |
Disapproval |
Surprise + Sadness |
Hope |
Anticipation + Trust |
Unbelief |
Surprise + Disgust |
Anxiety |
Anticipation + Fear |
Outrage |
Surprise + Anger |
Love |
Joy + Trust |
Remorse |
Sadness + Disgust |
Guilt |
Joy + Fear |
Envy |
Sadness + Anger |
Delight |
Joy + Surprise |
Pessimism |
Sadness + Anticipation |
Submission |
Trust + Fear |
Contempt |
Disgust + Anger |
Curiosity |
Trust + Surprise |
Cynicism |
Disgust + Anticipation |
Sentimentality |
Trust + Sadness |
Morbidness |
Disgust + Joy |
Awe |
Fear + Surprise |
Aggressiveness |
Anger + Anticipation |
Despair |
Fear + Sadness |
Pride |
Anger + Joy |
Shame |
Fear + Disgust |
Dominance |
Anger + Trust |
Combinations
Human feelings |
Emotions |
Opposite feelings |
Emotions |
Bemusement |
Interest + Serenity |
Dismay |
Distraction + Pensiveness |
Zeal |
Vigilance + Ecstasy |
Horror |
Amazement + Grief |
Acknowledgement |
Serenity + Acceptance |
Listlessness |
Pensiveness + Boredom |
Devotion |
Ecstasy + Admiration |
Shame |
Grief + Loathing |
Acquiescence |
Acceptance + Apprehension |
Impatience |
Boredom + Annoyance |
Subservience |
Admiration + Terror |
Hatred |
Loathing + Rage |
Wariness |
Apprehension + Distraction |
Disfavor |
Annoyance + Interest |
Petrification |
Terror + Amazement |
Domination |
Rage + Vigilance |
Advanced Emotions
Dimensions |
High Sensitivity |
Low Sensitivity |
High Pleasantness |
Low Pleasantness |
High Attention |
Aggressiveness |
Anxiety |
Optimism |
Frustration |
Low Attention |
Rejection |
Awe |
Frivolity |
Disapproval |
High Aptitude |
Rivalry |
Submission |
Love |
Envy |
Low Aptitude |
Contempt |
Coercion |
>Gloat |
Remorse |
Neurobiological factors
Estrogen

Individual differences in women's estrogen cycles may be related to the expression of BPD symptoms in female patients. A 2003 study found that women's BPD symptoms were predicted by changes in estrogen levels throughout their menstrual cycles, an effect that remained significant when the results were controlled for a general increase in negative affect.